Software development costs can often exceed initial estimates as products become more intricate and user expectations rise. However, there are ways to reduce these costs without compromising quality, innovation, or standards.
Efficient teams demonstrate daily that delivering high-quality software while managing costs is achievable. The key lies in identifying where time, resources, and effort are being misallocated.
Unnoticed inefficiencies, ambiguous requirements, and unnecessary complexities can inflate costs before they are detected. Addressing these areas strategically not only saves money but also enhances development speed, product stability, and team productivity.
This article delves into practical strategies for cutting software development costs without compromising user expectations. Whether you are a startup stretching limited resources or a large enterprise optimizing extensive projects, implementing these tactics will help you build more efficiently and effectively.
Key Takeaways
- Emphasize eliminating waste, streamlining workflows, and ensuring all efforts add tangible product value to reduce software development costs effectively.
- Costs escalate with project complexity, suboptimal technology decisions, unclear team communication, and poorly managed infrastructure or testing requirements.
- Hidden expenses like scope expansion, technical debt, communication overheads, API integrations, compliance, maintenance, and technical support quietly inflate budgets.
- Implement intelligent methods such as Agile, MVP-first development, automation, open-source tools, code reuse, and continuous optimization to lower software development costs.
Key Factors That Affect Software Development Cost
The cost of software development varies based on factors like project complexity, chosen technologies, team composition, experience, and location. Clear requirements, efficient project management, infrastructure needs, testing depth, and contingency planning also impact the final budget.
1. Project Complexity
The complexity of a software project significantly influences development costs. Features, user roles, integrations, and workflows require specialized skills, extensive testing, and increased effort as complexity rises.
Coordinating complex projects becomes more challenging, demanding additional resources to ensure stability and performance. More intricate products result in higher development costs.
2. Technology Stack
The technology stack chosen, including programming languages, frameworks, tools, and services, can affect development costs. Some technologies require rare skills, leading to higher salaries, while others introduce licensing fees or setup delays.
Selecting technologies strategically prevents compatibility issues, rework, and costly maintenance in the future. Early technology decisions can avoid unnecessary expenses and ensure smoother long-term development.
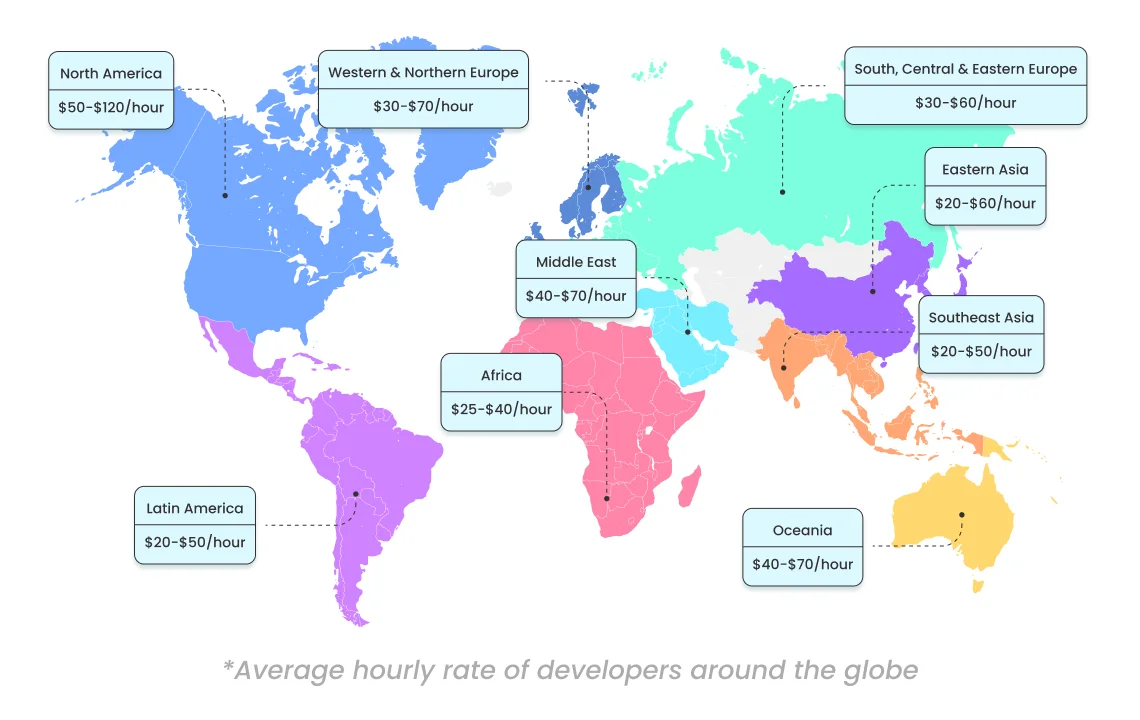
3. Team Composition & Location
The size, experience, and location of the development team directly impact the budget. Hiring developers and specialists from countries with lower living costs can save money. Effective hiring reduces long-term expenses and produces high-quality work.
However, location differences can pose communication challenges that need proper management to prevent delays or misunderstandings that increase costs.
Optimizing infrastructure choices, including servers, cloud platforms, databases, and deployment tools, plays a significant role in development costs. Scalable cloud environments reduce long-term expenses, while inadequate configuration leads to overspending on unused resources.
Deployment pipelines, security setups, and monitoring systems add additional costs. Careful planning ensures the infrastructure supports the product effectively without unnecessary expenditure.
6. Quality Assurance & Testing
Quality assurance testing is crucial for building reliable software, with effort varying based on the product’s size and complexity. Larger systems require more test cases, automation, performance checks, and security validations.
Skimping on testing may lower immediate costs but often leads to higher expenses later due to bugs or user dissatisfaction. Proper quality assurance planning ensures stable releases and minimizes expensive rework.
7. Contingency Planning
Unforeseen issues like integration failures, scope changes, or technical constraints can raise development costs if contingency plans are absent. Allocating time and budget for potential risks helps teams stay prepared and maintain control when challenges arise.
Without adequate contingency planning, even minor disruptions can become costly setbacks affecting timelines and overall project success.

Effective Strategies for Software Development Cost Reduction
Reducing software development costs without compromising quality involves adopting Agile practices, prioritizing an MVP, reusing components, and leveraging automation. Cost-effective tools, skilled teams, optimized infrastructure, and strong vendor agreements further enhance the process. When consistently applied, these strategies make development more predictable, affordable, and impactful.
1. Adopt Agile Methodology
Agile methodologies help teams cut costs by breaking projects into manageable increments. This approach enhances visibility, speeds up feedback, and prevents extensive rework. Continuous delivery and rapid iteration ensure every development effort aligns with user needs, reducing waste and keeping the budget on track.
2. Build a Minimum Viable Product (MVP)
Developing an MVP allows quick validation of ideas without investing in full-scale features upfront. By focusing on core functionality, launching early, and gathering user feedback, overspending on unwanted features is avoided. An MVP ensures investment aligns with proven demand rather than assumptions.
3. Leverage Open-Source Tools
Using open-source frameworks, libraries, and tools significantly reduces licensing and development costs. These battle-tested, well-supported tools accelerate development by eliminating the need to build core components from scratch.
Choosing open-source technology wisely shortens time-to-market, lowers overall expenses, and provides flexibility without costly vendor lock-ins.
4. Automate Testing & Deployment
Automation reduces manual work, ensuring consistent, high-quality results. Automated testing identifies bugs early, preventing costly fixes later in the development cycle. Automated deployment pipelines streamline releases, minimize errors, and accelerate delivery.
These processes free up the team from routine tasks, allowing them to focus on valuable work, enhancing both efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
5. Outsource Strategically
Strategic outsourcing provides access to specialized skills without the long-term cost of full-time hires. When done correctly, it offers flexibility, scalability, and cost advantages, particularly for tasks requiring niche expertise.
Choosing the right outsourcing partner, ensuring clear communication, and setting measurable expectations are key. Strategic outsourcing reduces overhead, accelerates development, and maintains quality.

6. Reuse Code & Modular Architecture
Code reuse reduces development time and effort significantly. Building modular components for reuse across features or projects avoids duplication of work.
A modular architecture simplifies maintenance, testing, and scalability. Over time, this approach creates a library of reusable assets, cutting costs, enhancing consistency, and speeding up delivery.
7. Optimize Infrastructure Costs
Cloud resources, servers, and deployment environments can become major expenses if not monitored closely. Optimizing infrastructure involves auto-scaling, right-sizing resources, and eliminating unused services.
Choosing cost-effective cloud options and regularly auditing usage prevent unnecessary expenditure. Aligning infrastructure with actual needs ensures stability and efficiency without overspending.
8. Negotiate Contracts Well
Effective contract negotiation with vendors, cloud providers, or development partners can significantly reduce long-term costs. Clear pricing models, defined deliverables, and performance-based terms prevent hidden expenses and unexpected charges.
Good negotiation secures more value for the budget, maintaining cost-efficient relationships throughout the project.
9. Invest in Skill Development
Upskilling the team enhances productivity, reduces reliance on external consultants, and minimizes errors leading to costly rework. Updated with modern tools, frameworks, and practices, developers deliver higher-quality work faster.
Training investment may seem like an initial cost, but it pays off through improved efficiency, better performance, and lower long-term expenses.
10. Monitor Metrics & Continuous Optimization
Tracking key development metrics identifies inefficiencies before they become costly problems. Monitoring velocity, defect rates, cycle time, and resource usage provides a clear view of areas needing improvement.
Continuous optimization ensures the development process evolves with product and business needs. Small adjustments over time lead to significant cost savings and smoother delivery cycles.

Hidden Costs That Increase Software Development Budgets
Hidden costs like scope creep, onboarding and training expenses, communication overheads, technical debt, tooling and integrations, security and compliance requirements, and maintenance and support inflate software development budgets. These additional costs can lead to significant budget overruns if not managed effectively.
Scope Creep
Uncontrolled changes in project requirements can quickly escalate budgets. Each additional feature or modification requires extra development, testing, and integration, consuming resources not initially allocated.
Onboarding and Training Costs
Introducing new team members requires time, documentation, mentorship, and sometimes formal training. These costs, often underestimated, accumulate, especially in larger teams or projects with specialized technologies.
Communication and Coordination Overheads
Distributed teams, remote work, or cross-functional collaboration can create inefficiencies. Time spent in meetings, clarifying requirements, or resolving misunderstandings adds indirect costs impacting both budget and timeline.
Technical Debt and Rework
Rushed development or unclear requirements can lead to poorly written code, resulting in technical debt. Addressing these issues later requires rework, refactoring, and additional testing, all increasing project costs.
Tooling and Integration Expenses
Software licenses, plugins, platforms, and API integrations often come with hidden costs. Compatibility issues may require extra time and resources to resolve.
Security and Compliance
Ensuring software meets regulatory and security standards involves audits, certifications, and additional development work. Ignoring these requirements may save money initially but can lead to costly penalties or breaches later.
Maintenance and Technical Support
Ongoing maintenance, updates, and bug fixes require continuous developer involvement, adding recurring costs. Technical support for users, including troubleshooting and enhancements, also consumes resources not always budgeted initially. These long-term responsibilities expand project expenses if not planned from the start.